We know what we want to say. We can explain it out loud just fine. But when we sit down to write, the words stall.
This is a translation block. Our brain can't turn thought into text. Studies show long pauses (5+ seconds) between sentences. Once typing starts, speed is normal.
What Is Composition Block?
It hits at the translation stage. Ideas exist, but sentences won't form. This is stage 2 in the writing process: Planning, then Translation, then Revision.
Behavioral Signs
- Long pauses (5+ seconds) between sentences
- Normal speed once a sentence starts
- Smooth bursts within each sentence
- Few edits or cuts while drafting
How common: About 40% of writers have this problem. It is most common in new writers and those writing in a second language. New genres like op-eds or academic prose also trigger it.
Why Translation Is Hard
When we build a sentence, we juggle many tasks at once:
- Meaning (what to say)
- Grammar (how to say it)
- Word choice (which words fit)
- Tone (formal or casual)
- Genre rules (style needs)
- Flow (links between sentences)
Working memory holds about 7 items. When the load gets too high, the process breaks down.
Speech has fewer rules. We get live feedback from listeners. We use gestures and tone. Writing adds typing, visual checks, format rules, and the stress of making words last.
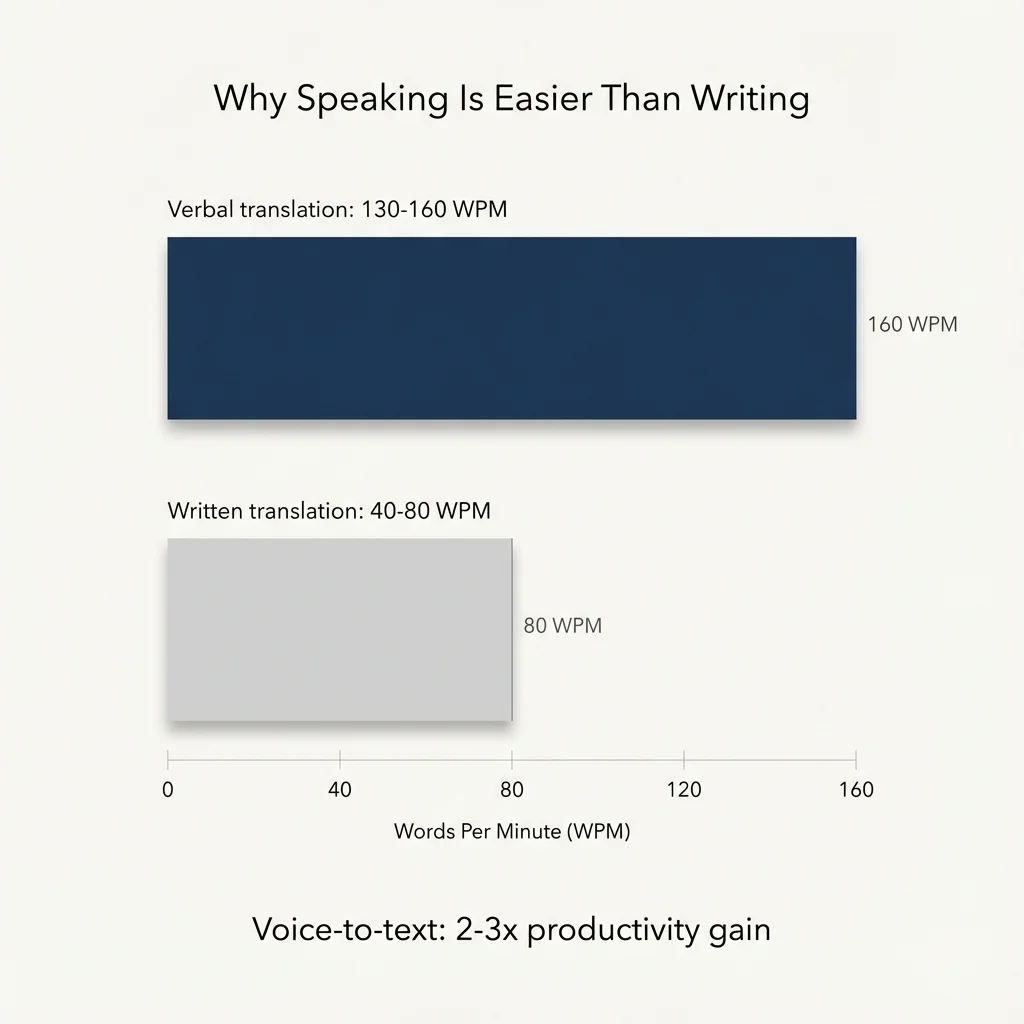
Cooper and Matsuhashi (1982) found that voice-to-text raised output by 2-3x.
Evidence-Based Interventions
Tier 1: Strong Evidence
- We speak at 130-160 words per minute
- We type at 40-80 words per minute
- Result: 2-3x more output
- Today's tools: 95%+ correct for clear speech
How to start:
- Pick a tool (phone app, software, or unstoppable.ink)
- Make a short outline
- Talk as if telling a friend
- Casual speech works best. Skip perfect grammar.
- Let the tool type for us
- Edit the text later (2-4 hours or next day)
- Set a 5-minute timer before writing
- Say the idea out loud (to a person, a recorder, or a rubber duck)
- Keep talking. Do not stop to fix phrasing.
- Write right after speaking
- Result: 30-50% more output after oral warm-up
- Use subject-verb-object order
- One main idea per sentence
- Cap drafts at 15 words per sentence
- Use periods, not commas, to split big ideas
- Join sentences later during editing
Tier 2: Some Evidence
- Write as an email: Email tone is more casual. This frees up working memory.
- Use short sessions: Draft for 20 minutes, break for 10. This stops burnout.
What Does Not Work
- "Outline more": Outlines do not fix the translation step
- "Read more": That is a long-term fix for a short-term problem
- "Take a break": Rest helps with fatigue, not translation
- "Just start writing": This skips the real issue
8-Week Implementation Protocol
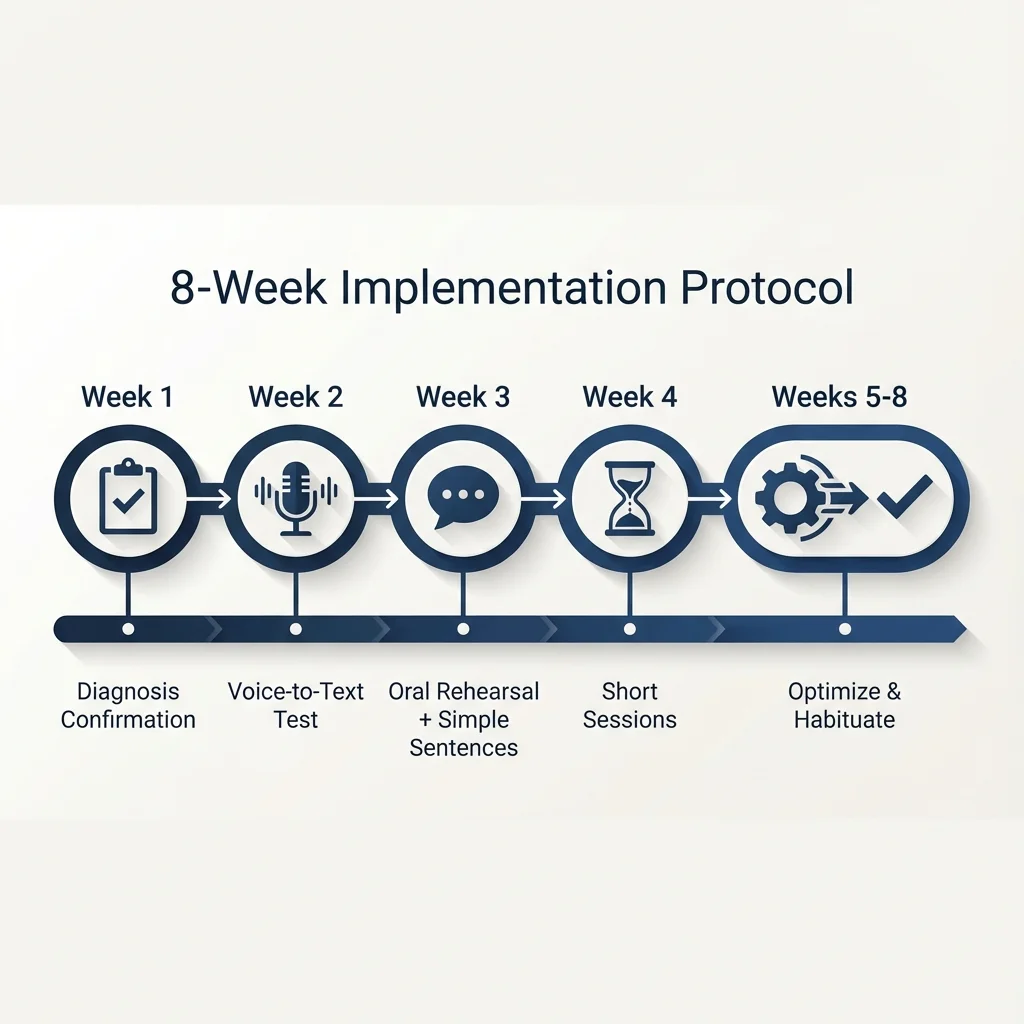
Week 1: Check the Problem
Track pauses during 3 sessions. Check that the longest pauses fall between sentences. Compare speech output to typed output.
Week 2: Try Voice-to-Text
Skip typing. Dictate instead. Compare the two methods.
Week 3: Talk First, Then Write Simply
Speak the idea for 5 minutes. Then write with short, simple sentences.
Week 4: Short Sessions
Write for 20 minutes. Break for 10. Track what happens within each session.
Weeks 5-8: Build the Habit
Pick the best method. Make it a routine. Aim for 30-50% gain over Week 5 levels.
Translation trouble is a skill gap. It does not reflect our smarts or talent. With the right tools, it gets better.