Research shows that language skill, not coding, predicts success with AI. Writers already have the core skills that drive good prompting.
The Evidence: Writing Skills Predict AI Success
Word variety links to AI output quality at r=0.444. Language skill explains 17% of the gap in coding learning results. 83.7% of users said clarity helps AI results.

These results suggest that skills writers build over years (precision, clarity, knowing the reader) transfer to AI work. This is one of the best cases for why writing still matters in the AI age.
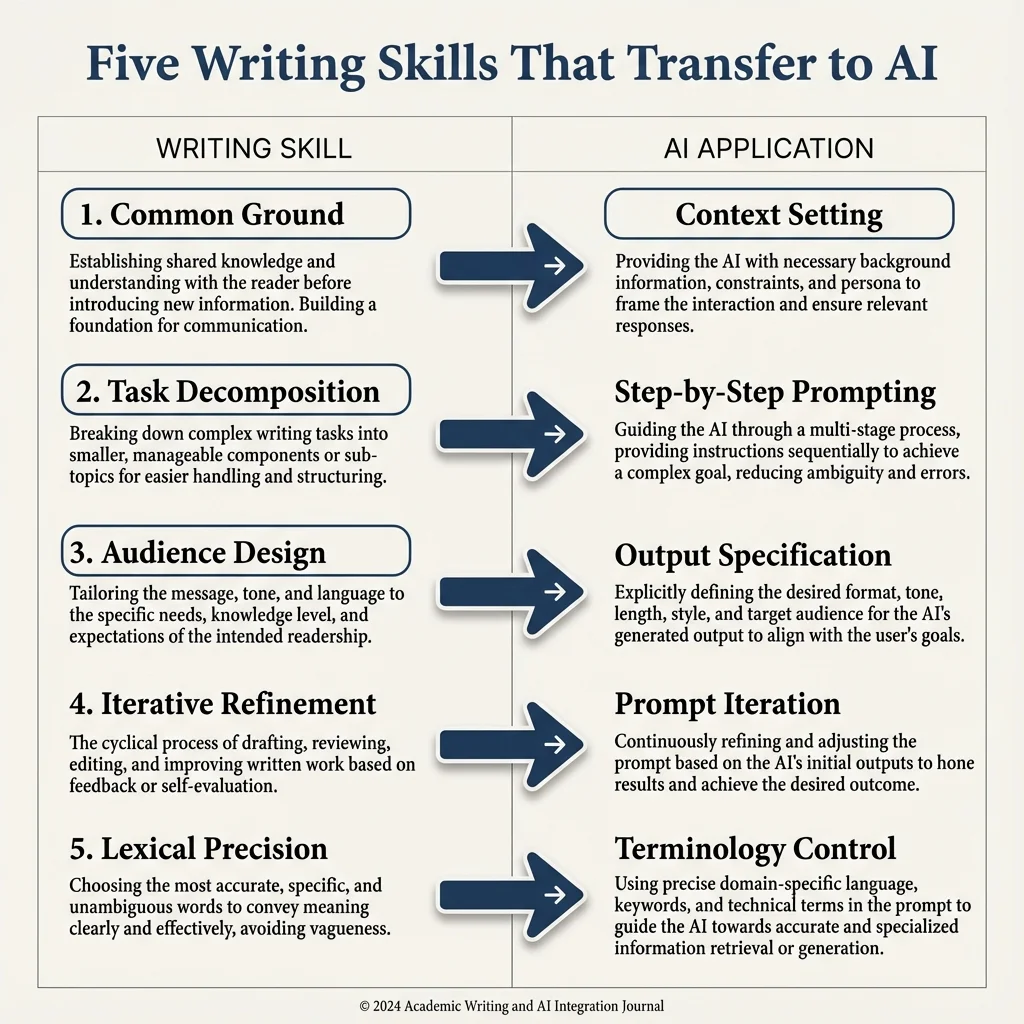
The Five Writing Skills That Transfer
1. Common Ground Establishment
Good writers already set up context for readers. LLMs need the same thing: context, clear terms, and shared facts before the main request.
2. Task Decomposition
Writers outline hard projects before drafting. "Chain of Thought" prompting mirrors this. It breaks hard requests into steps that guide the AI through the logic.
3. Audience Design
Writers adjust tone for different readers. With AI, setting a persona (write as an expert for beginners, or as a peer for experts) steers the output the right way.
4. Iterative Refinement
The revision process maps right onto AI work. Treat AI output as a first draft that needs critique and a new prompt. The back-and-forth improves results just as revision improves writing.
5. Lexical Precision
Specific words push models away from generic replies. The more precise our language, the more precise the AI's reply. This is the link captured in the r=0.444 finding.
Writing as a Domain-General Cognitive Skill
Writing skill works as "High Road Transfer" to AI work. The core skills of clarity, structure, and precision transfer across settings because they solve basic communication problems.
Writers tend to prompt AI better than coders. They have spent years building the language precision that matters most.
How to Leverage Writing Skills
- Check our prompts like writing: Before hitting send, review the prompt as we would review any draft
- Set limits: Give word counts, style guides, and format rules to steer the output
- Review what failed: When output falls short, ask why. Was the context unclear? The request vague? Were limits missing?
- Use back-and-forth: Treat AI work as a series of rounds, not a single shot
The core insight: prompt writing is not a new tech skill to learn. It uses skills writers already have. The word choice, clarity, and structured thinking that make writing work also make prompts work. For a hands-on guide, see writing practice through AI prompting.